What is Bitcoin Mining? And What Happens When the Final BTC is Mined!

Bitcoin (BTC) - The king of crypto, the world's first and most powerful digital currency, was created as a decentralized monetary system that operates without banks or third parties. The key role for this system is Bitcoin mining - the process of both generating new BTC and protecting the network by verifying every transaction. Without it, Bitcoin would lose its transparent, unmanipulated structure - which has made the world trust it.
Now, more than 95% of all Bitcoins have been mined, with less than 1.1 million BTC left to drip over the next 100 years. This makes many people wonder: "What will happen when 21 million Bitcoins are mined dry?"
This article will help you decode everything, from basic knowledge about coin mining to the future vision of Bitcoin when the supply reaches its maximum threshold. And don't forget to guide you how to store and protect BTC absolutely safely with Bitget Wallet.
What is Bitcoin Mining?
Simply put, Bitcoin mining is the process of validating transactions and recording them on the blockchain, while creating new BTC. Miners use mining machines to race to solve extremely complex problems based on the Proof-of-Work mechanism. Whoever solves it first will have the right to add a new block of transactions to the chain and receive a reward in Bitcoin.
By doing both of these things - verifying transactions and issuing new coins in a controlled manner - Bitcoin mining is considered the backbone of the entire Bitcoin ecosystem.
Why is Mining Important?
Bitcoin mining plays several vital roles in the network:
-
Network security:
Mining ensures that the blockchain cannot be altered or hacked, as changing transaction history would require immense computational power.
-
Fraud prevention:
By validating every transaction, mining prevents double spending, ensuring Bitcoin maintains its integrity as digital money.
-
Issuance of new BTC:
Mining gradually releases Bitcoin into circulation, creating a predictable, transparent supply schedule.
Read more: Exploring the BTC Ecosystem: A Comprehensive Analysis
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
Bitcoin mining is the process that keeps the network stable and secure through solving computational challenges:
-
Difficulty Adjustment
The protocol adjusts mining difficulty every 2016 blocks (~2 weeks) to maintain an average block time of about 10 minutes.
-
Mining Computation
Specialized ASIC hardware executes trillions of hashes per second, altering block header fields (nonce, timestamp, extraNonce, nVersion) until a valid hash meets the target.
-
Security Through Hashrate
This global competition in hashrate prevents tampering with Bitcoin’s ledger, making attacks prohibitively expensive.
Inside a Bitcoin Block
A block is composed of:
-
Block Header:
Includes the version, hash of the previous block, Merkle root (summary of all transactions), timestamp, compressed difficulty (bits), and nonce.
-
Transactions:
Features a special coinbase transaction, which issues new BTC and collects transaction fees for the miner. Coinbase outputs can only be spent after 100 confirmations.
Mempool & Transaction Selection
Miners choose which transactions to include, prioritizing those with the highest fee rates (satoshis/vByte) while adhering to the block weight cap of ~4 million units under SegWit.
Propagation & Forks
If two blocks are mined at nearly the same time, a temporary fork may occur. The chain with the most accumulated proof-of-work (the “longest chain rule”) becomes canonical, while the other block is orphaned. Each subsequent block adds one confirmation to previous transactions, with ~6 confirmations generally viewed as secure for high-value transfers.
Block Rewards & Transaction Fees
Each mined block rewards the miner with:
- Newly created BTC (block subsidy)
- Transaction fees from included transactions
The subsidy is cut in half every 210,000 blocks (~4 years) in a process called Bitcoin halving:
- 2009: 50 BTC/block
- 2012: 25 BTC/block
- 2016: 12.5 BTC/block
- 2020: 6.25 BTC/block
- 2024: 3.125 BTC/block (current reward)
This programmed decline creates Bitcoin’s built-in scarcity, a key driver of its long-term value.
What is Bitcoin Halving and the Supply Limit?
The core value of Bitcoin is tied to its scarcity. Unlike fiat currencies, which central banks can print indefinitely, Bitcoin is programmed directly into its code to ensure that its supply will always remain fixed.
To control issuance and mimic the scarcity of precious resources like gold, Bitcoin employs a mechanism called the halving.
21 Million BTC Cap
Bitcoin was designed with a hard cap of 21 million BTC, meaning its total supply will never exceed this limit. This scarcity shapes its role in the global financial system:
-
Finite supply:
The absolute cap makes Bitcoin fundamentally different from fiat currencies, which can be printed without limit.
-
Digital gold:
Scarcity positions Bitcoin as a long-term store of value, much like gold in traditional finance.
-
Inflation hedge:
A fixed supply makes Bitcoin a potential safeguard against currency debasement and excessive money printing by central banks.
Bitcoin Halving History
Bitcoin halving occurs roughly every four years, cutting the mining reward in half. This event gradually slows the issuance of new BTC and increases scarcity over time:
- 2009 launch: 50 BTC per block.
- 2012 halving: 50 → 25 BTC.
- 2016 halving: 25 → 12.5 BTC.
- 2020 halving: 12.5 → 6.25 BTC.
- 2024 halving: 6.25 → 3.125 BTC (current reward).
- 2028 projection: 3.125 → 1.5625 BTC.
These halvings will continue until around the year 2140, when the last fraction of a Bitcoin is mined. Each halving has historically been followed by a surge in Bitcoin’s price, as supply issuance drops while demand often increases.
Read more: What is the Bitcoin Halving and Why Should You Care?
How Much Bitcoin is Left to Mine?
As of 2025, more than 94–95% of all Bitcoins have been mined – that’s about 19.9 million BTC. That leaves just under 1.1 million BTC left, and it will take more than 100 years to mine them all.
That may sound like a lot, but these remaining BTC are actually the rarest of the lot – the most valuable digital assets the crypto world has been waiting for.
Why is the Remainder Small but Stretches to 2140?
The answer lies in the Halving mechanism – every 4 years, the Bitcoin mining reward is cut in half. As a result, the rate at which new Bitcoins are created slows down:
📉 By around 2035, 99% of Bitcoins will have been mined.
⏳ It will take more than 100 years to mine even the remaining 1%!
As a result, Bitcoin retains predictable scarcity, making it increasingly similar to “digital gold” – a truly deflationary asset.
What Happens When All 21 Million BTC Are Mined?
When the very last Bitcoin is mined — expected around the year 2140 — the dynamics of the network will change forever. No new BTC will enter circulation, meaning Bitcoin will achieve its final, fixed supply status.
End of Block Rewards in Bitcoin Mining
Currently, miners receive two sources of income:
- Newly minted BTC (block subsidy)
- Transaction fees.
But once the cap of 21 million BTC is reached, no new coins will be created. The subsidy portion of mining rewards will drop to zero.
Miners’ Future Income After Bitcoin Mining Ends
At that stage, miners’ only incentive will come from transaction fees.
- If transaction demand is high, fees could become lucrative, ensuring miners remain incentivized to secure the network.
- If demand is low, mining might become less profitable, potentially leading to weaker network security.
This transition makes transaction activity — and thus Bitcoin’s role in the global economy — more important than ever.
Impact on the Bitcoin Network
The post-mining era will bring significant implications:
- Transaction fees may rise, especially during high demand.
- Layer-2 solutions like the Lightning Network will become essential for scalability and cheaper transactions.
- Bitcoin will likely shift even further toward being viewed as “digital gold” — a long-term store of value rather than an everyday payment medium.
Challenges and Opportunities for Bitcoin in the Post-Mining Era
The end of mining subsidies will reshape the Bitcoin ecosystem, creating both risks and growth opportunities:
| Challenges | Opportunities |
| Network security risk when block rewards disappear, making miners solely dependent on transaction fees. | Ultra-scarcity of Bitcoin could increase its value significantly. |
| Mining centralization as only large, efficient mining operations can survive. | Shift to green mining and renewable energy solutions may strengthen Bitcoin’s sustainability. |
| Environmental pressure from continued energy-intensive Proof-of-Work mining. | Layer-2 solutions, sidechains, and Bitcoin DeFi expand BTC’s usability beyond a store of value. |
How to Buy Bitcoin (BTC) on Bitget Wallet?
Buying Bitcoin (BTC) on Bitget Wallet is easy! Just follow these simple steps:
Step 1: Create a wallet
- If you don't have a wallet, download Bitget Wallet app now.
- Register with your phone number or email, verify quickly and you can use it right away.
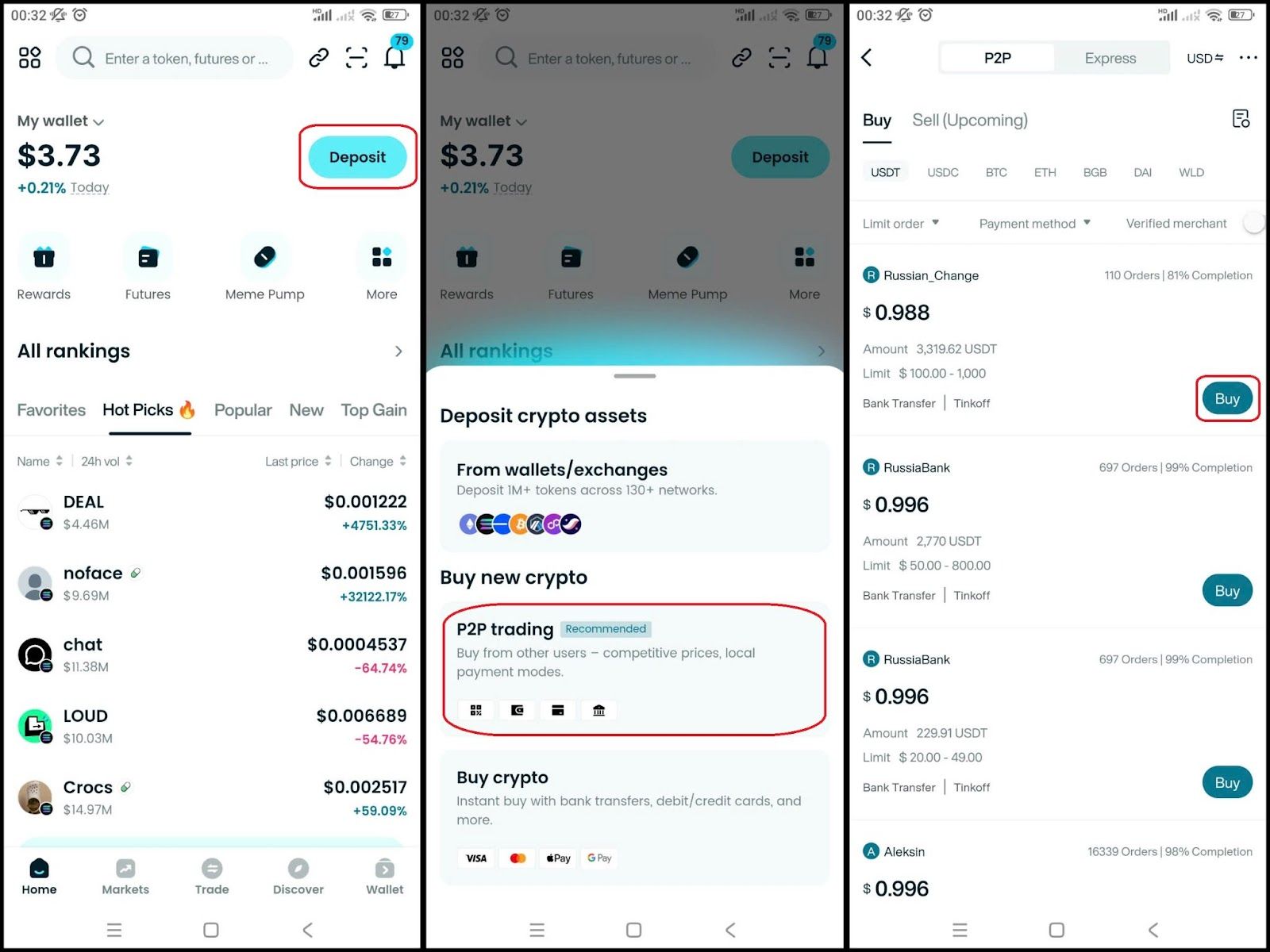
Step 2: Deposit money into your wallet
Once you have finished creating your wallet, you just need to deposit money into it. You can:
- Transfer coins from other wallets: Send BTC, ETH or any coin you have from an external wallet.
- Buy directly with a card: Use a bank card or credit card to buy USDT or ETH right in the app and then exchange it for BTC.
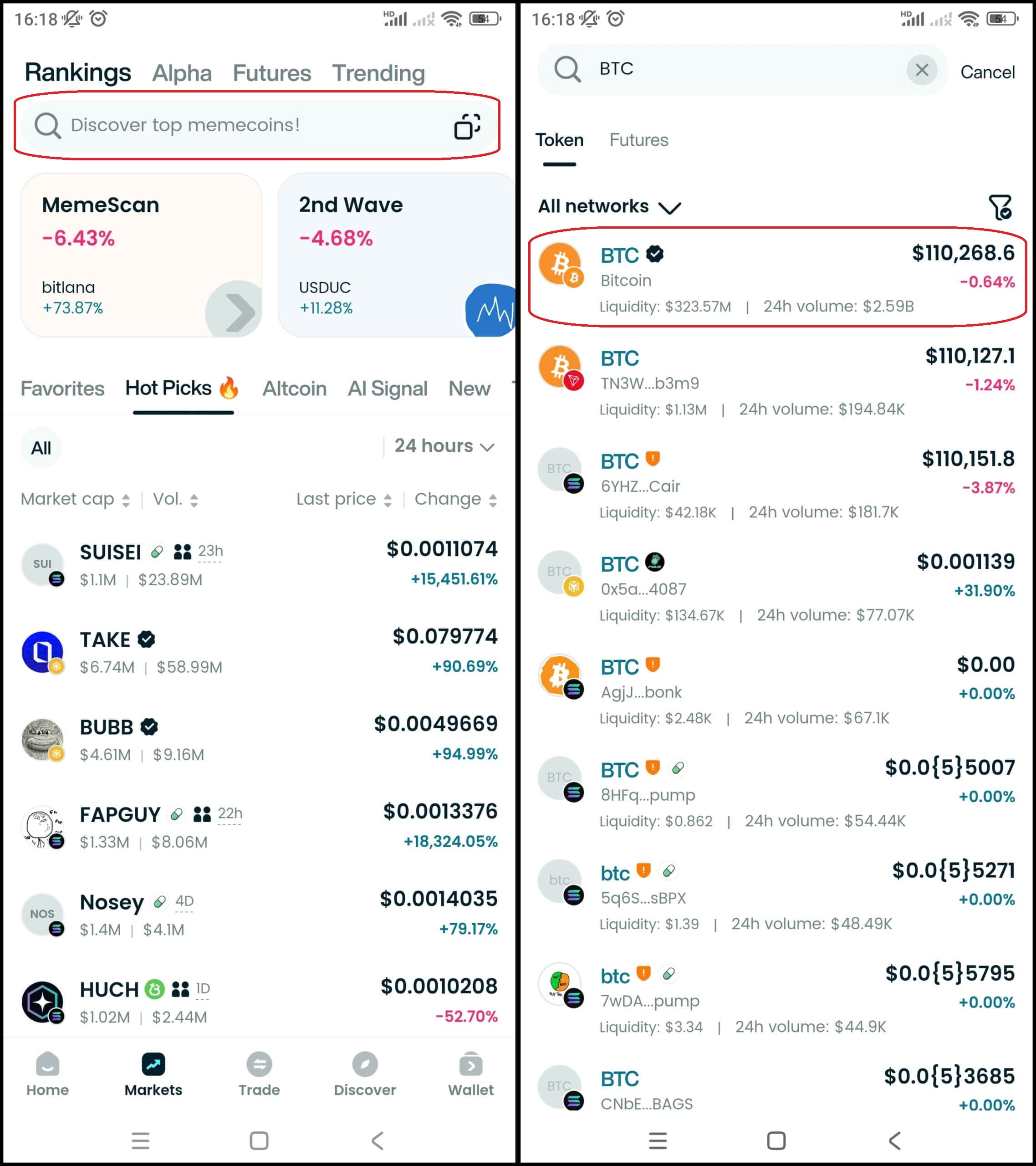
Step 3: Find Bitcoin (BTC)
- In the main interface of the wallet, go to Market, type Bitcoin or BTC in the search bar.
- Select Bitcoin (BTC) to see the trading page.
Step 4: Select the trading pair
Select the pair you want to trade, for example BTC/USDT. This means you can use USDT to buy Bitcoin (BTC), or sell BTC back to USDT.
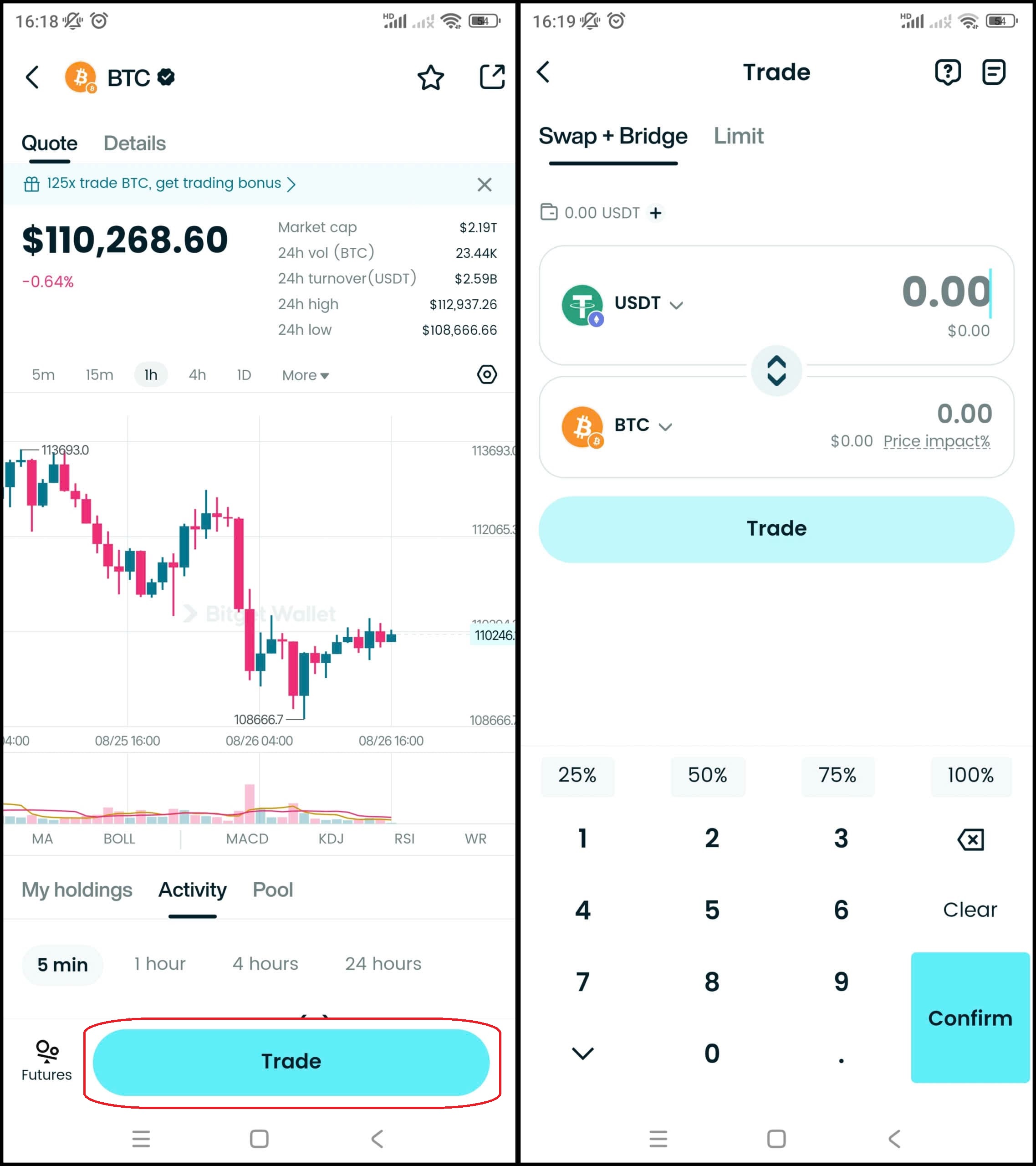
Step 5: Place an order
Enter the amount of Bitcoin (BTC) you want to buy, check carefully and confirm the order.
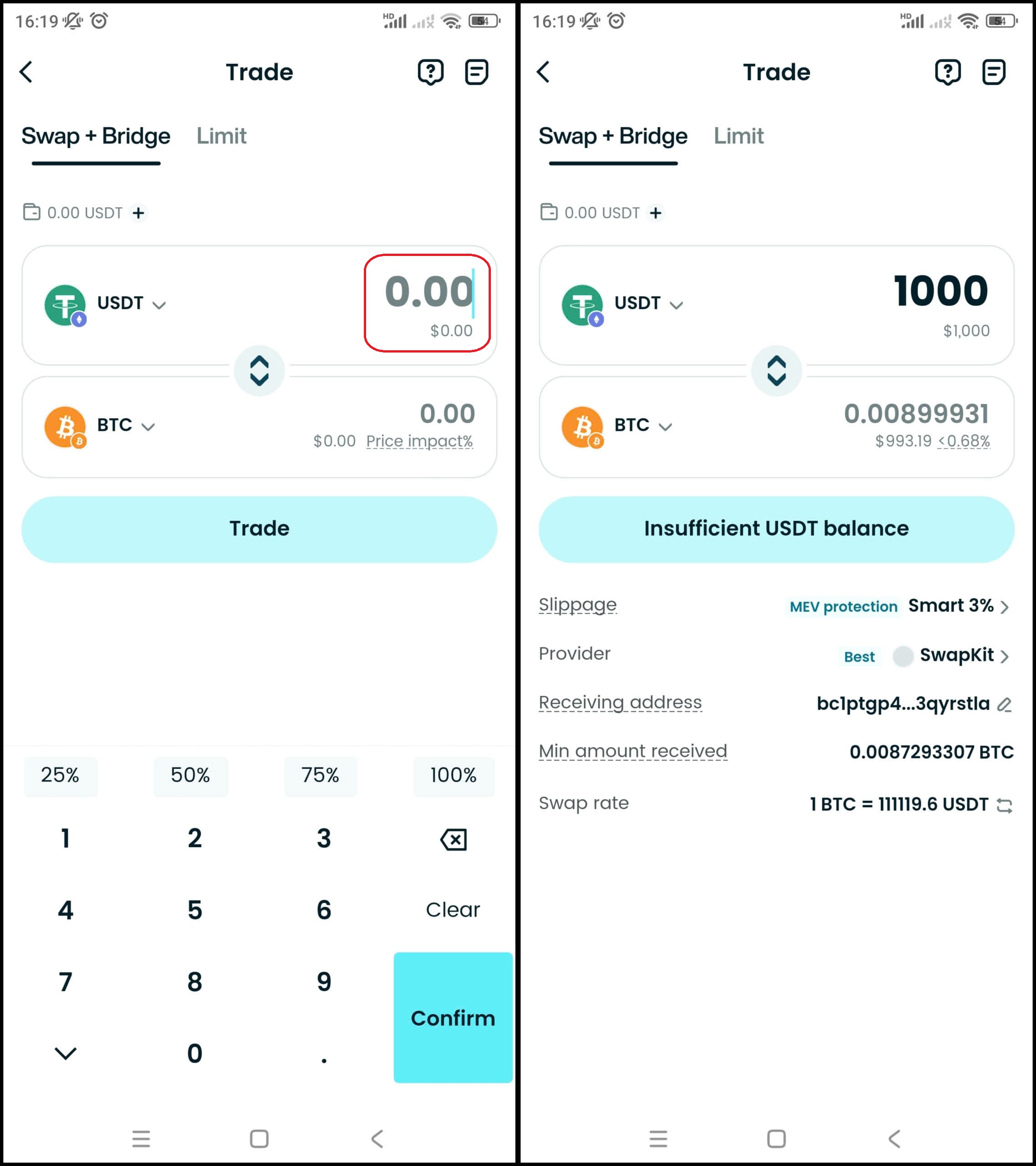
Step 6: Check the order
After buying, you can check your Bitcoin (BTC) in the Wallet section.
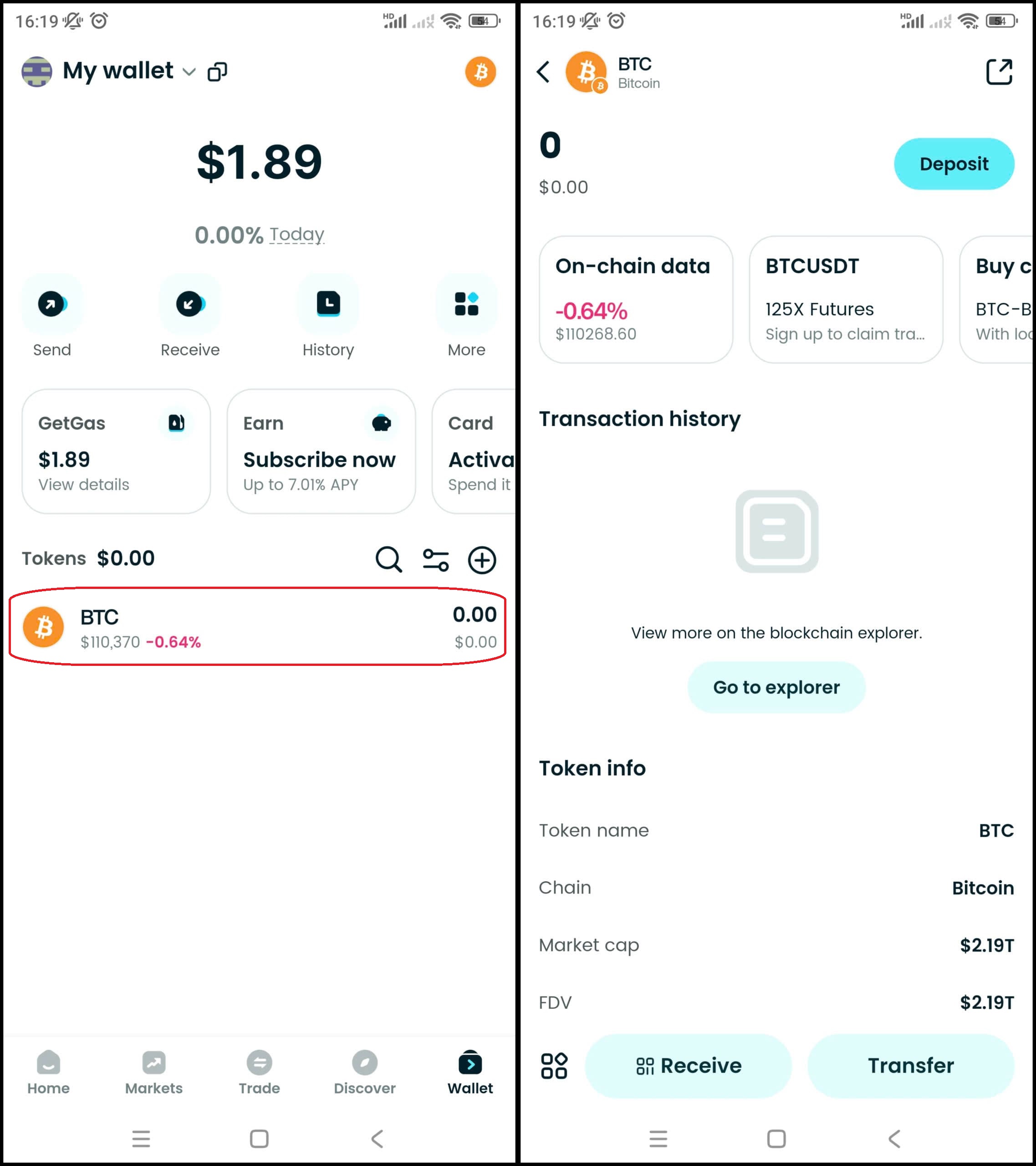
Step 7: Withdraw (if needed)
Once you have Bitcoin (BTC), if you want to withdraw to another wallet, go to Withdraw, fill in the receiving wallet address, check the blockchain network and the amount carefully, then confirm.
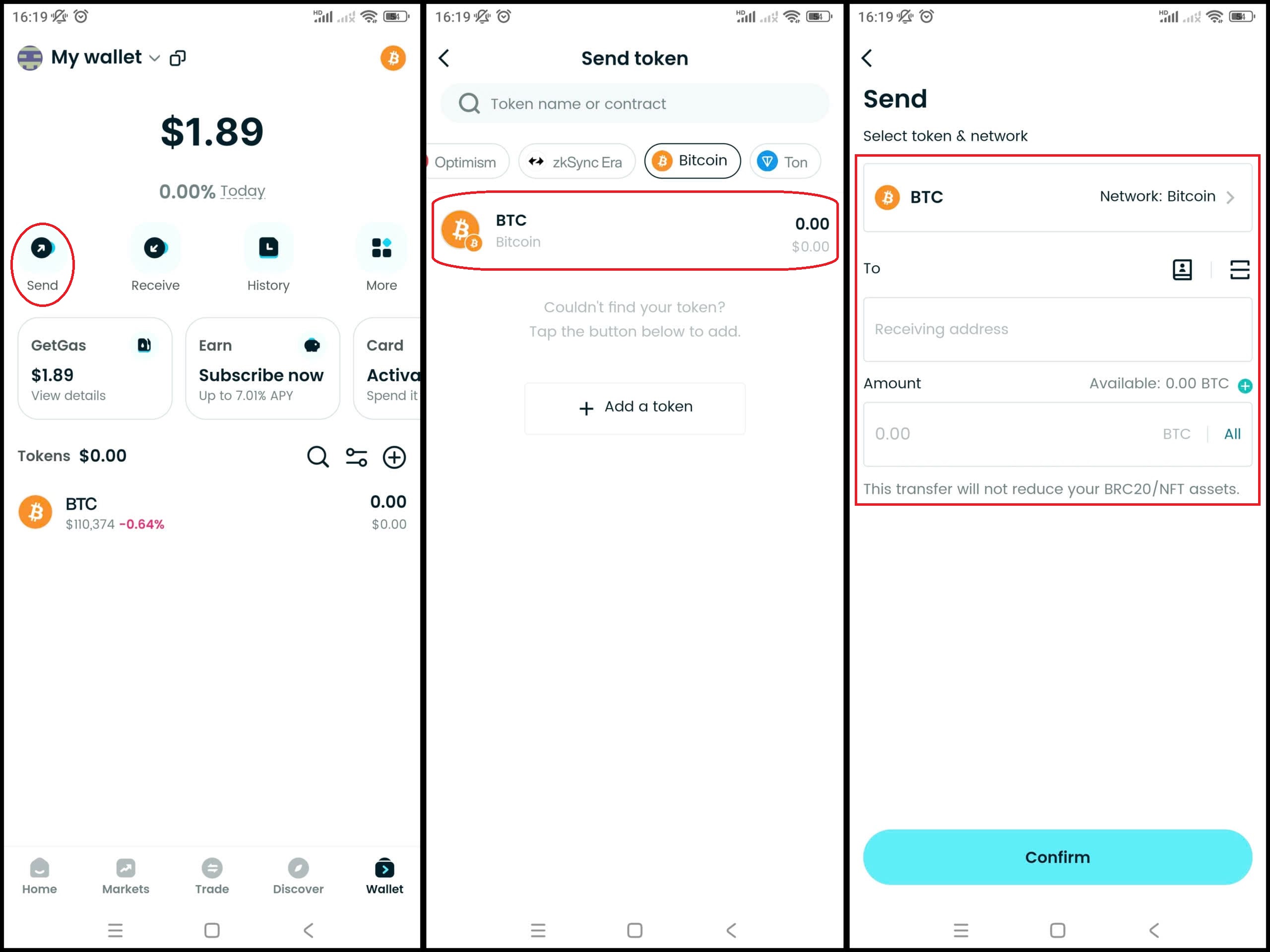
▶ Learn more about Bitcoin (BTC):
- What is Bitcoin (BTC)?
- MetaMask vs Bitget Wallet: Which Is Better in 2025?
- Trust Wallet vs Bitget Wallet: Which One Is Better in 2025?
- Phantom vs Bitget Wallet: Which One Is Better?
Conclusion
Bitcoin mining is not just about creating new BTC - it also serves as the backbone of the network, ensuring decentralization, trust, and resilience. With over 95% of all Bitcoins already mined and less than 1.1 million BTC remaining to be released by 2140, the focus is now shifting from “creation” to “custody”. The real question is no longer “What is Bitcoin mining?”, but “How do you protect your BTC for the future?”.
As Bitcoin approaches its supply limit, security and custody solutions become key. Bitget Wallet offers state-of-the-art encryption, MPC (Multi-Party Computation) smart wallet technology with no single point of failure, along with the assurance of 24/7 support and a $300 million Security Fund. Combined with multi-chain access and seamless DeFi integration, it gives us the ability to fully protect and grow our Bitcoins in the digital era.
Download Bitget Wallet today to take full control of your Bitcoins.
Sign up Bitget Wallet now - grab your $2 bonus!
FAQs
1. What is Bitcoin mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process by which powerful computers (called miners) solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions on the network, then add them to a public ledger (the blockchain). The reward for those who solve that problem is BTC.
2. What happens to miners when no new Bitcoin is mined?
When all 21 million BTC are mined, miners will no longer receive block subsidy. Instead, their main source of income will come from transaction fees that users pay to prioritize their transactions. At this point, the security of the network will depend entirely on transaction activity.
3. Which is the best BTC wallet?
Bitget Wallet is the best BTC wallet - featuring advanced MPC security technology, flexible multi-chain support, and fully integrated features from storage, trading to staking. In particular, Bitget Wallet is backed by a $300 million Protection Fund, providing maximum peace of mind for users.
Risk Disclosure
Please be aware that cryptocurrency trading involves high market risk. Bitget Wallet is not responsible for any trading losses incurred. Always perform your own research and trade responsibly.


















